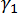 )
)
Skew is a measure of asymmetry in the distribution. A positive skew indicates a longer tail to the right, while a negative skew indicates a longer tail to the left. A perfectly symmetric distribution, like the normal distribution, has a skew equal to 0. For small data sets this measure is unreliable.
Population Skew (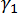 )
)
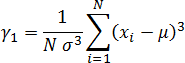
Sample Skew (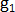 )
)
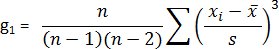
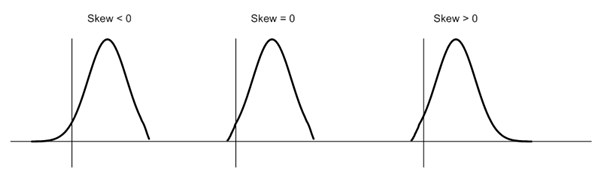
(adapted from King and Julstrom, 1982 and Hildebrand, 1986)
where
|
|
|
|
s |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
N |
= number of data values for a population |
|
n |
= number of data values for a sample |
|
xi |
= ith data value |
See Also
95% and 99% Confidence Interval for the Mean
Critical Value of K-S Statistic at 90%, 95%, and 99% Significance Level
Kolmogorov-Smirnov Goodness of Fit Statistic for Normal Distribution